In this blog post, we explore the CTO salary range; separately for the United States and the United Kingdom. We are examining variations and influencing factors across public and private companies as well as start-ups, fast-growth firms and large enterprises. Additionally, we’ll look into the most common bonus structures of a Chief Technology Officer position.
And, don’t worry; we’re going to keep this short and straightforward.
NOTE: All the figures are based on the reports of the people who reportedly are or have been working as Chief Technology Officers. We are, however, talking about hundreds of reports after all so they must be close to the real numbers.
Let’s start with analysing the highest-paying sectors this year. If you are looking for a Chief Technology Officer job, this could easily influence your decision.
Now, let’s check the averages separately for private and public companies in the US.
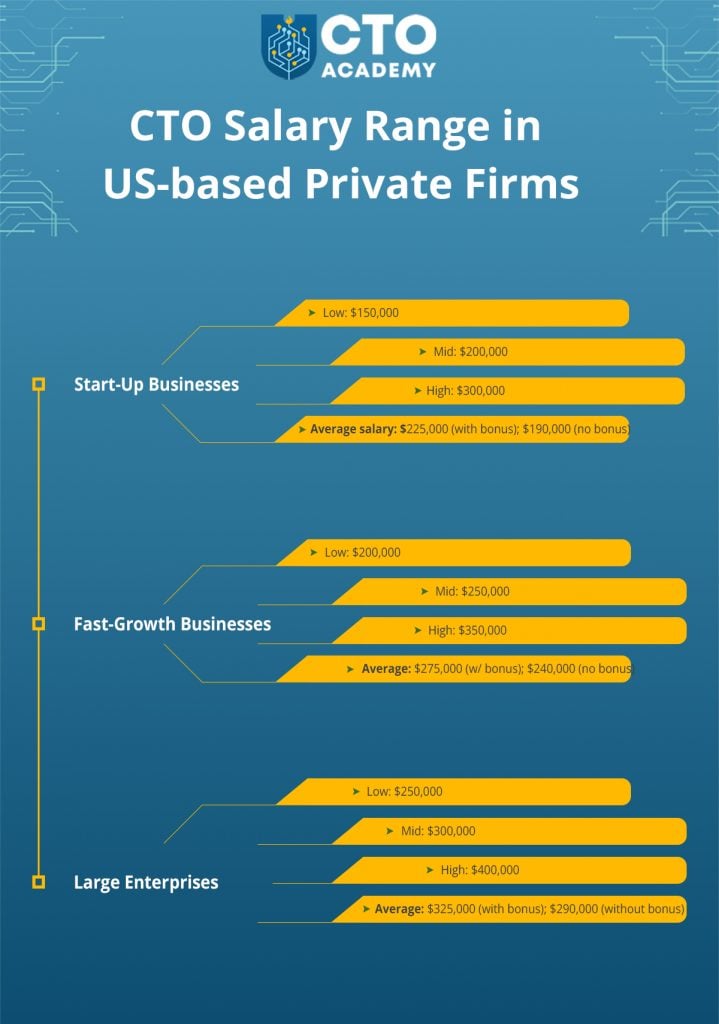
Start-ups
Average salary: $225,000 (with bonus); $190,000 (without bonus)
Fast-growth companies
Average: $275,000 (with bonus); $240,000 (without bonus)
Large enterprises
Average: $325,000 (with bonus); $290,000 (without bonus)
Start-ups
Average: $225,000 (with bonus); $190,000 (without bonus)
Fast-growth companies
Average: $275,000 (with bonus); $240,000 (without bonus)
Large enterprises
Average: $325,000 (with bonus); $290,000 (without bonus)
Sources: Salary.com, Payscale, Indeed
The highest-paying sector for Chief Technology Officers (CTOs) in the UK is software, with an average salary of £174,503. The lowest-paying industry is retail, with an average of £172,843.
According to Glassdoor, these are the highest payers:
Differences are almost insignificant. Let’s now break down these averages to private and public businesses and government institutions.

Start-ups
Average: £125,000 (with bonus); £100,000 (without bonus)
Fast-growth companies
Average: £175,000 (with bonus); £150,000 (without bonus)
Large enterprises
Average: £225,000 (with bonus); £200,000 (without bonus)
If we now compare public companies, we will see the same ranges – just like it’s the case with US companies.
Start-ups
Average: £125,000 (with bonus); £100,000 (without bonus)
Fast-growth companies
Average: £175,000 (with bonus); £150,000 (without bonus)
Large enterprises
Average: £225,000 (with bonus); £200,000 (without bonus)
Sources: Salary.com, Payscale, Indeed, Glassdoor CTO salary
And in case you’ve been wondering…
Salary.com cites $512,800 while the query on Glassdoor returns $465,109. Somewhere within the mid-range are Payscale and Indeed with $492,276 and $487,514 respectively.
Looking for more? Okay, here it comes…
The average CTO Salary at Google
The salary of a Chief Technology Officer at Google varies depending on the experience, skills and location. According to Glassdoor, the average base salary is $350,000. However, the total package can be much higher, in some instances reaching well over $500K by some estimates.
What about those bonuses that can double the salary? What types are most commonly available to Chief Technology Officers?
Bonuses play a crucial role in remuneration, reflecting performance, achievements and contributions. They come in several forms:
Performance-based bonuses
Performance-based bonuses, typically paid annually, tie the CTO’s pay to specific metrics, such as revenue growth, product development milestones or successful technological implementations.
On average this bonus can add to the base salary up to 2.5-7.5%. It can, however, go as high as 15% in some instances. For example, a Chief Technology Officer in a Fortune 500 company with a base salary of $500,000 could expect to receive a performance-based bonus of $12,500 to $37,500. If the CTO’s performance is exceptional, they could receive a bonus of up to $50,000.
Equity-based bonuses
An equity-based bonus, often seen in start-ups and private companies, grants a Chief Technology Officer ownership stake in the company. As the company grows and its valuation increases, the CTO’s equity can become a substantial source of wealth.
A good example is Andy Bechtolsheim, a co-founder of Sun Microsystems and a former CTO of the company. From the IPO in 1986, the company reached $1 billion in sales by 1988. Along with the base salary, Bechtolsheim also had an equity-based bonus. After the IPO, as the company’s value was increasing, so was Bechtolsheim’s equity value.
Retention Bonuses
A retention bonus encourages a Chief Technology Officer to stay with the company for a certain period. These bonuses are particularly prevalent in situations where a company is undergoing a transition or facing challenges.
Here’s a couple of examples of conditions attached to retention bonuses:
Several factors influence the salary ranges for CTOs. Some, like the size of a company, industry and geographic location we already saw. But there are also two additional ones that can affect the pay regardless of these three. They are:
In other words, an experienced Chief Technology Officer working in a company that has a product with high market demand can make more regardless of the company’s size and location.
These salary insights help you understand the factors that influence remuneration and the intricacies of common bonus structures. You should now be able to add missing elements to your decision-making process and, ultimately, decide where you see yourself in the future. This is particularly important if you’re stepping into the CTO shoes from a software engineering position. Now you know the difference between your median pay as a software engineer and what you can expect in the executive role.
CTO Academy is here to help you better understand how to become a CTO who enjoys all the financial benefits of this top executive role. After all, the salary is primarily determined by your efficacy and not that much by the location or the size of the company. If nothing else, highly skilled CTOs can always search for something better.
90 Things You Need To Know To Become an Effective CTO

London
2nd Floor, 20 St Thomas St, SE1 9RS
Copyright © 2024 - CTO Academy Ltd